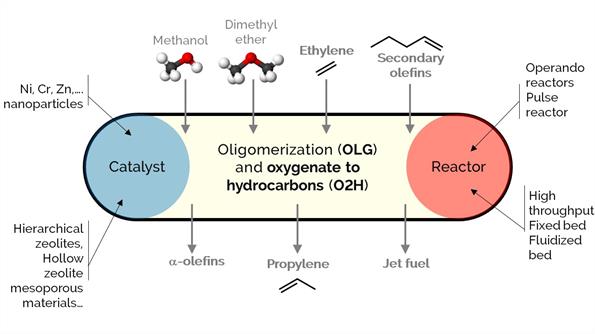
Olefins are commodity chemicals with applications in the production of plastics (petrochemical industry), lubricants, plasticizers, and surfactants, among many others. However, there is an imbalance between their production and demand, which oligomerization-cracking reactions over zeolites could solve. At the same time, zeolites are excellent catalysts for methanol to hydrocarbons (MTH), olefins (MTO), or aromatics (MTA). The processes aim to produce light hydrocarbons like propylene or convert ethylene into higher-value a-olefins, aromatic hydrocarbons (BTX), and jet fuel.
Our focus in this project is to modify, synthesize and develop novel materials of different porosity (engineered at the multiscale): from hierarchical zeolites, nano zeolites, and hollow zeolites to catalytic particles, bodies, spray-dried and extrudates with tuned properties. Additionally, we incorporate different metals (i.e., Ni, Cr, Zn) to adjust the selectivity of desired products.
We use various reactors, such as operando or high-throughput packed-bed and batch reactors.