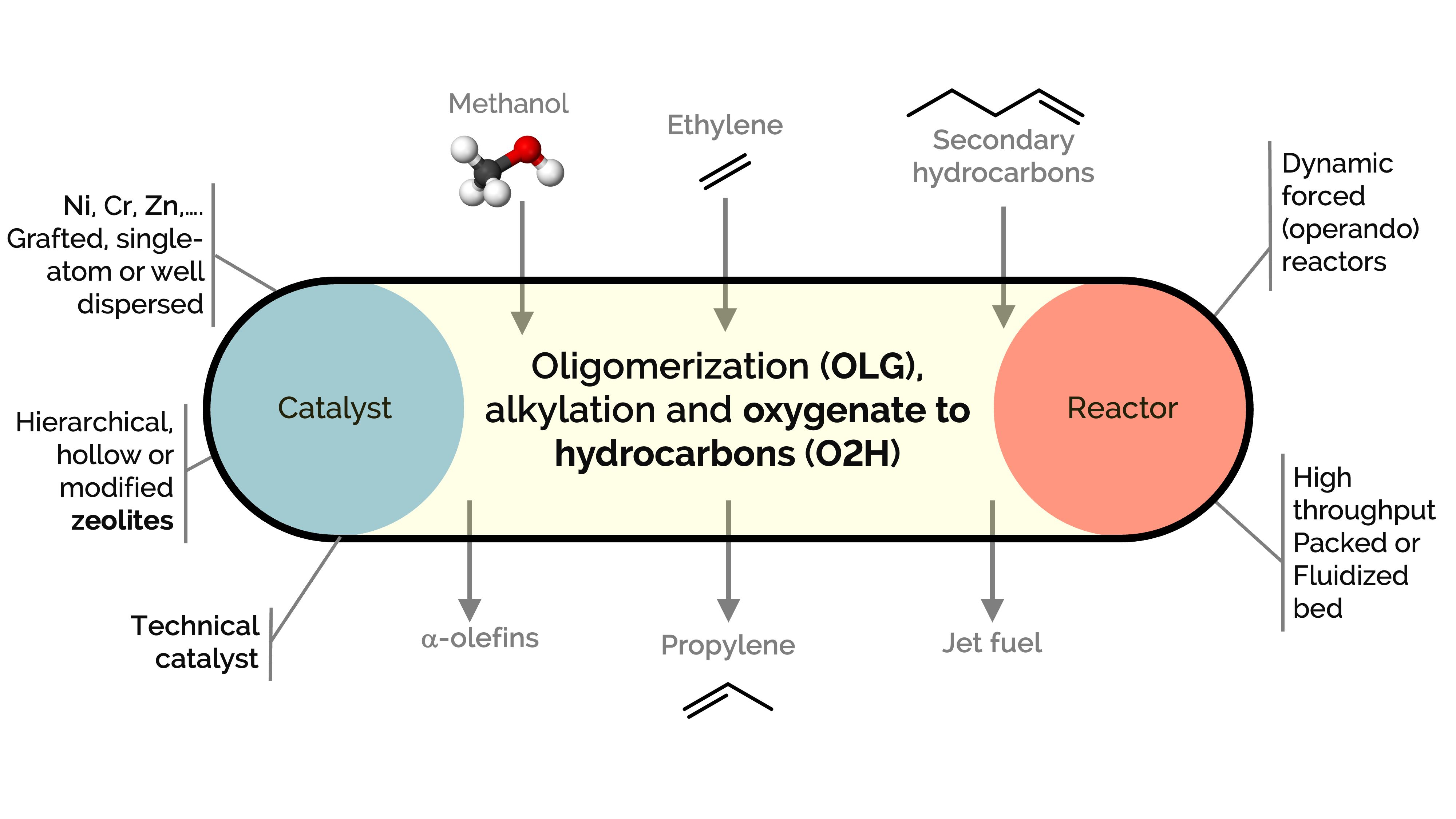
Olefins and aromatics are commodity chemicals used in producing plastics (in the petrochemical industry), lubricants, plasticizers, and surfactants, among other products. However, there is an imbalance between their production and demand, which reactions like oligomerization, alkylation, and cracking over zeolites could help address. At the same time, zeolites serve as excellent catalysts for converting methanol to hydrocarbons (MTH), olefins (MTO), or aromatics (MTA). These processes aim to produce light hydrocarbons such as propylene or to convert ethylene into higher-value alpha-olefins, aromatic hydrocarbons (BTX), and jet fuel.