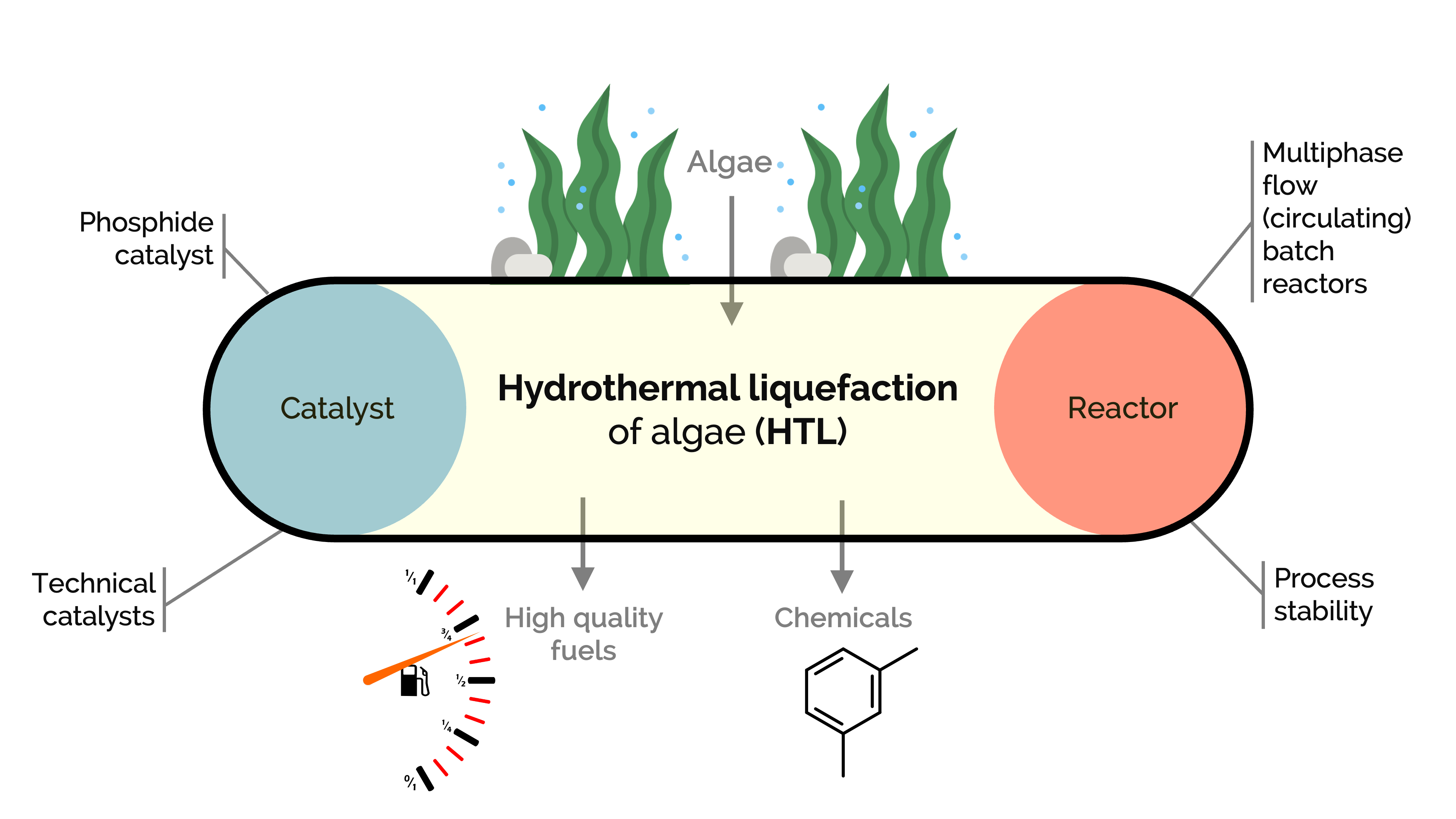
Algae are a rapidly growing, renewable biomass source rich in lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates, offering potential for biofuel and platform chemical production. Traditional bio-oil extraction often requires energy-intensive drying and solvent steps, which produce waste and limit economic viability. Hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL) can directly convert wet algae into bio-oil without drying, but the resulting product has high nitrogen and oxygen levels that reduce fuel quality. Additionally, HTL generates aqueous byproducts that are usually discarded, despite being nutrient-rich composition.