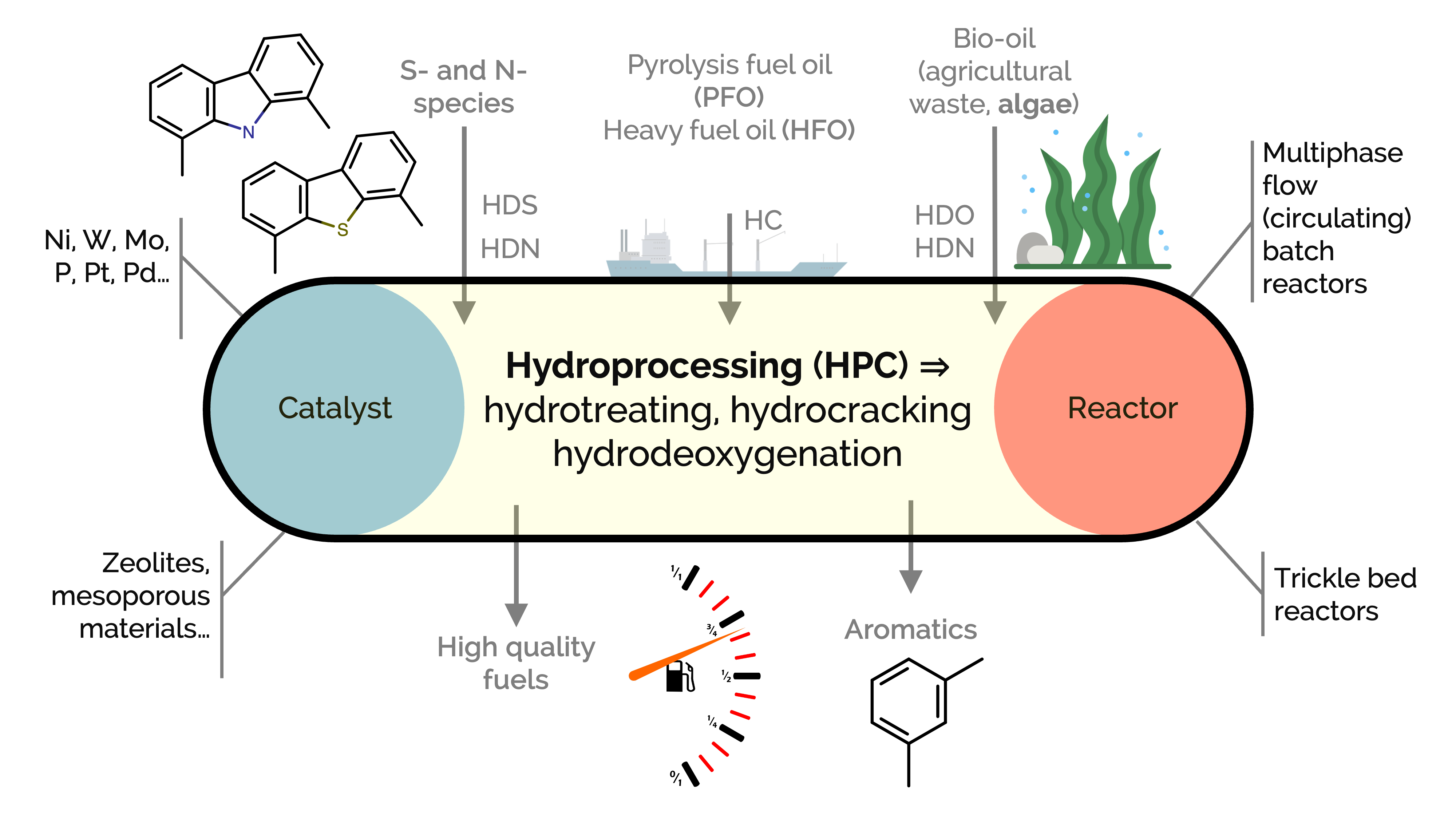
Hydroprocessing is a well-implemented and versatile refinery conversion strategy, comprising a wide array of reaction routes such as: (i) hydrotreating, aiming for the hydrogenation of unsaturated hydrocarbons and the removal (hydrogenolysis) of heteroatoms such as sulfur or nitrogen; (ii) hydrocracking, for promoting C–C bond scission and the partial saturation of aromatics; or (iii) hydrodeoxygenation, for the specific removal of oxygen moieties. In this project, we investigate the conversion of highly polyaromatic feedstocks, such as heavy fuel oil (HFO), pyrolysis fuel oil (PFO), and bio-oils from different biomass sources (e.g., agricultural waste, algae), to improve quality and produce products with higher added value.
We seek new (thermo-) catalytic strategies and improved heterogeneous catalysts with increased activity and stability. We apply advanced analytical characterization techniques (e.g., nuclear magnetic resonance, high-resolution mass spectrometry (FT-ICR MS)) and combine their results with modeling and statistical tools.