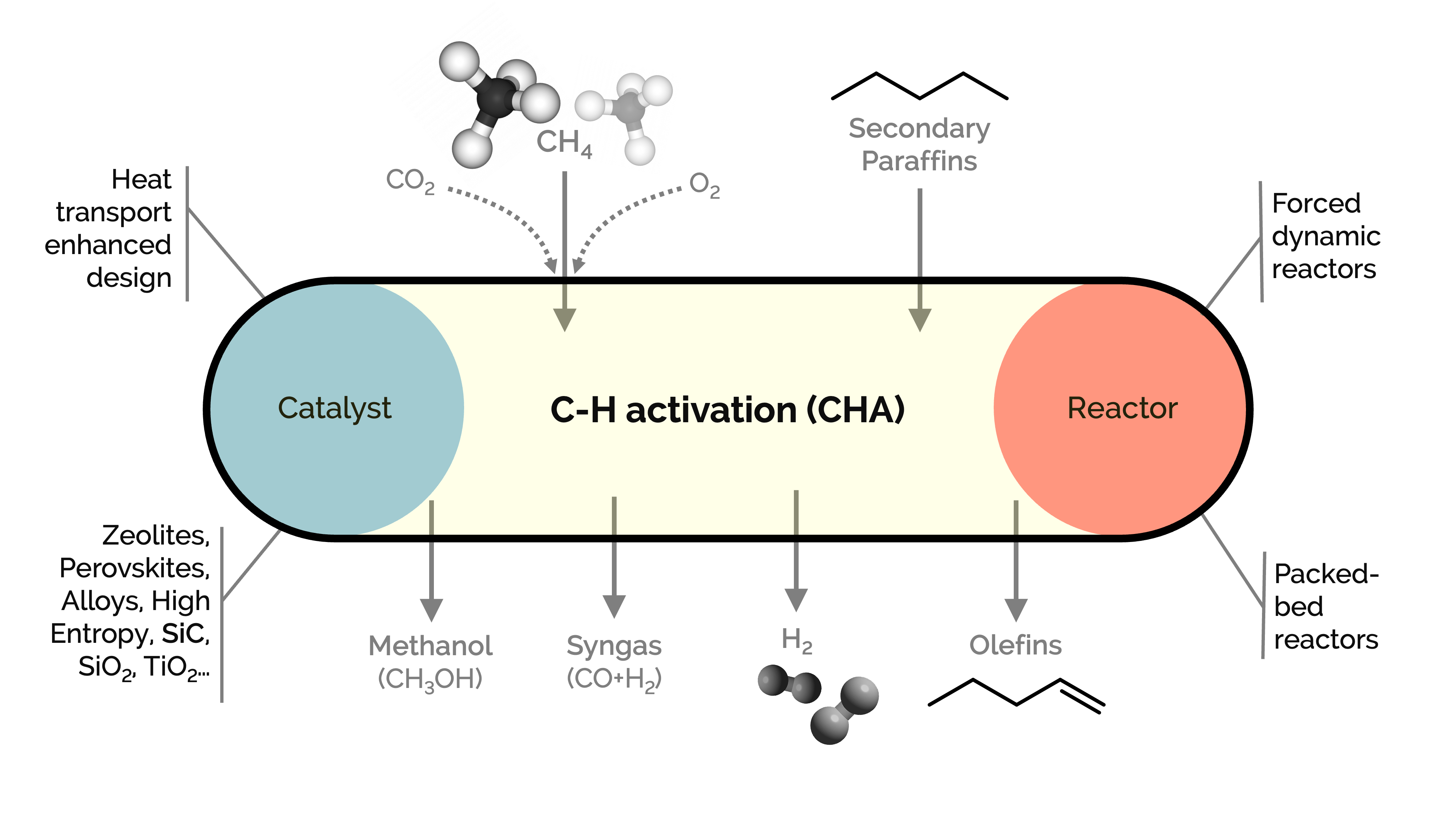
Methane and light alkanes are species with relatively poor economic interest. Our goal is to activate C–H σ-bond to produce hydrogen, olefins, carbon monoxide, and carbon nanofibers, following different process strategies such as oxidative coupling (for olefins), CO2 dry reforming (for syngas), cracking or catalytic decomposition (for hydrogen-free of COx and sequestrated carbon nanotubes/nanofibers), cracking/co-cracking with CO or methanol. We work on developing, synthesizing, characterizing, and testing innovative catalysts with a twist of reaction engineering concepts, with a focus on multi-scale implications.
We delve into the mechanistic insights into a series of in-house-synthesized metal-supported heterogeneous catalysts by combining them with dynamic reactors and ab initio calculations. We explore catalysts with extended lifetimes, enhanced activity, selectivity, and heat transfer. These catalysts are based on alloys-intermetallics, high entropy alloys, exsolved perovskites, and SiC, among others.
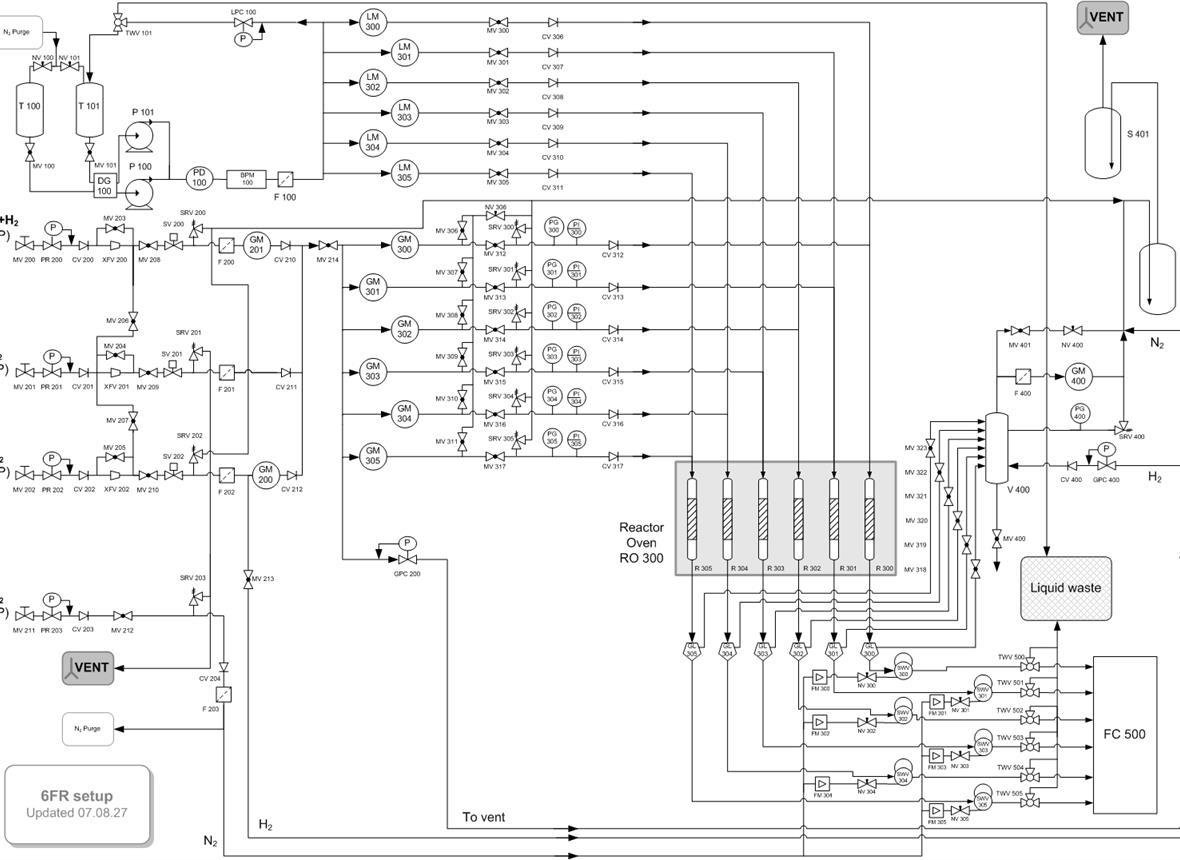
We investigate novel reactor designs based on forced-dynamic, operando, and fluidized-bed reactors to amplify kinetic information and improve selectivity.