We envision multiscale modeling as critical enablers of reaction understanding, catalyst and reactor design, scale-up, and process optimization. The framework includes predicting the molecular reaction mechanism at the molecular level to the process optimization stage. As catalytic processes occur at the multiscale, we address these issues individually and collectively.
At the microkinetic level, our models resolve the rates of the individual elementary steps, rate-determining step (RDS), adsorption, and desorption mechanisms. We use quantum chemical calculations (density functional theory, DFT) to support our assumed kinetic pathways, original parameter estimations, and adsorption-desorption energies.
We incorporate thermodynamic constraints into our models. Once developed, the microkinetic model could guide the catalyst and reactor design. We also have experience developing Langmuir-Hinshelwood and Eley-Rideal types of kinetic models.
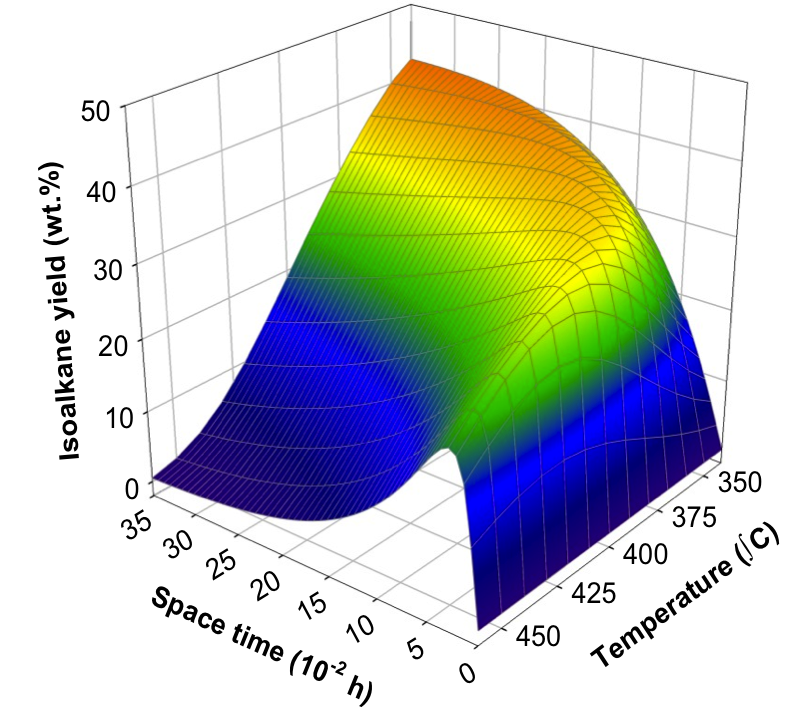
At the macrokineitc level, we develop lump-based and empirical models which, in some cases, are very robust and, together with other models, can be used to extract information such as mechanism change, optimize conditions, or for reactor pre-design.
We couple hydrodynamics, heat transfer, and reaction kinetics at the reactor level in computational fluid dynamic (CFD) simulations. Together with optimization algorithms, we aim to improve operating scenarios, develop innovative reactor prototypes, and predict process behaviors at the industrial scale.