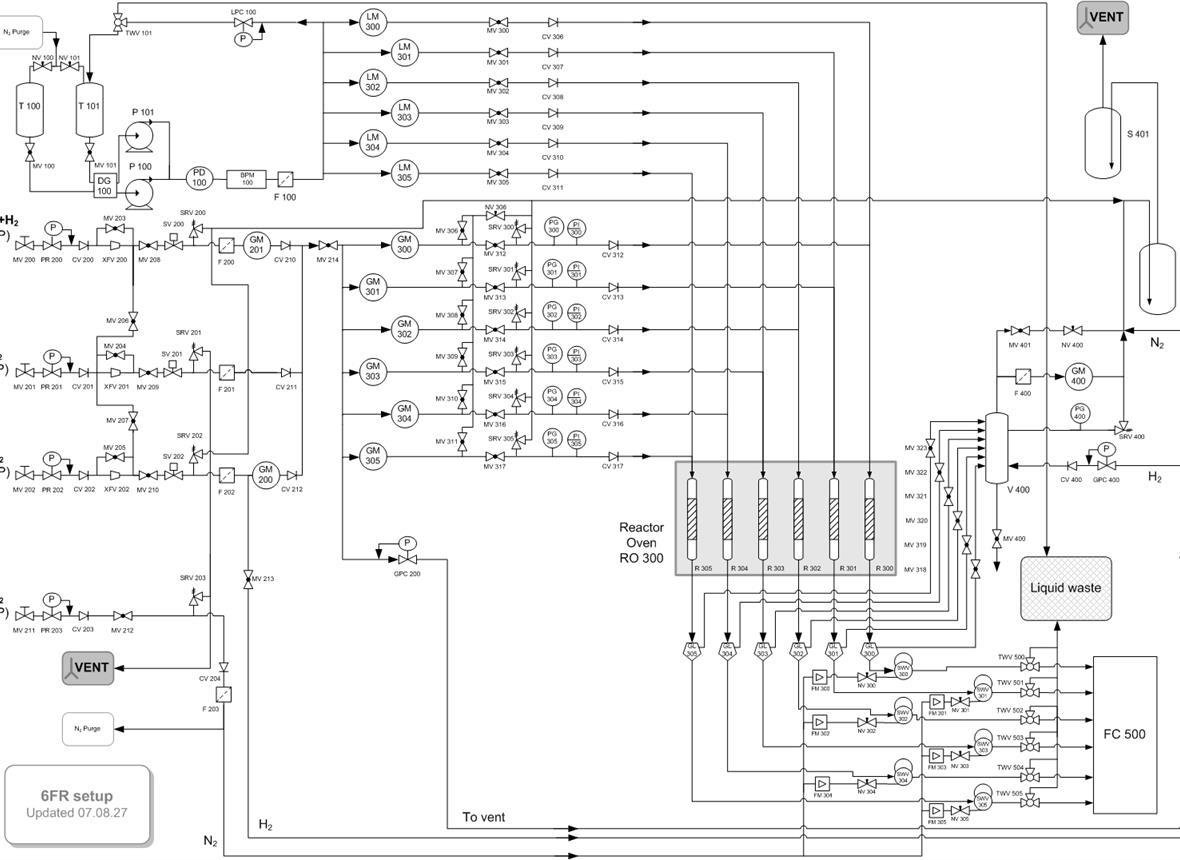
The catalytic cracking of high‐density polyethylene (HDPE) is an attractive process to valorize wastes throughout the production of the original monomers or fuels.
1 The cracking catalyst based on zeolites is able to drive the scission of the polymeric chain, while controlling the final selectivity of monomers or fuels.
2 The disadvantage of using a cracking catalyst is the deactivation caused by coke fouling, which hinders the cracking of heavy hydrocarbons and reduces the lifetime of the catalyst.
3