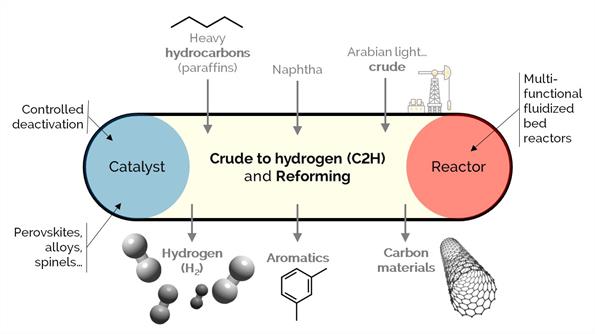
Hydrogen is a clean energy source and carrier because of its non−polluting combustion, making it an excellent alternative to the current fossil fuel-dominated energy scenario. Nonetheless, there are several critical challenges to implementing a broad sustainable use of hydrogen. In this project, we develop a laboratory−scale setup with stable operation and high hydrogen production.
We aim at assessing (i) different hydrocarbon feedstock (from n-heptane to crude oil) fed to the reactor with water as emulsions, carried by steam or vaporized; (ii) steam reforming (SR) and auto thermal reforming (ATR); and (iii) stable and energy efficient catalysts for the efficient production of hydrogen inside packed, fluidized, and multifunctional reactors. These, coupled with carbon capture technologies, minimize the carbon footprint of the overall process.
We support our research with simulations and techno−economic analysis to assess the approach's feasibility. C2H can use the current refinery infrastructure to reduce costs and the impact of market volatility on refinery operations.