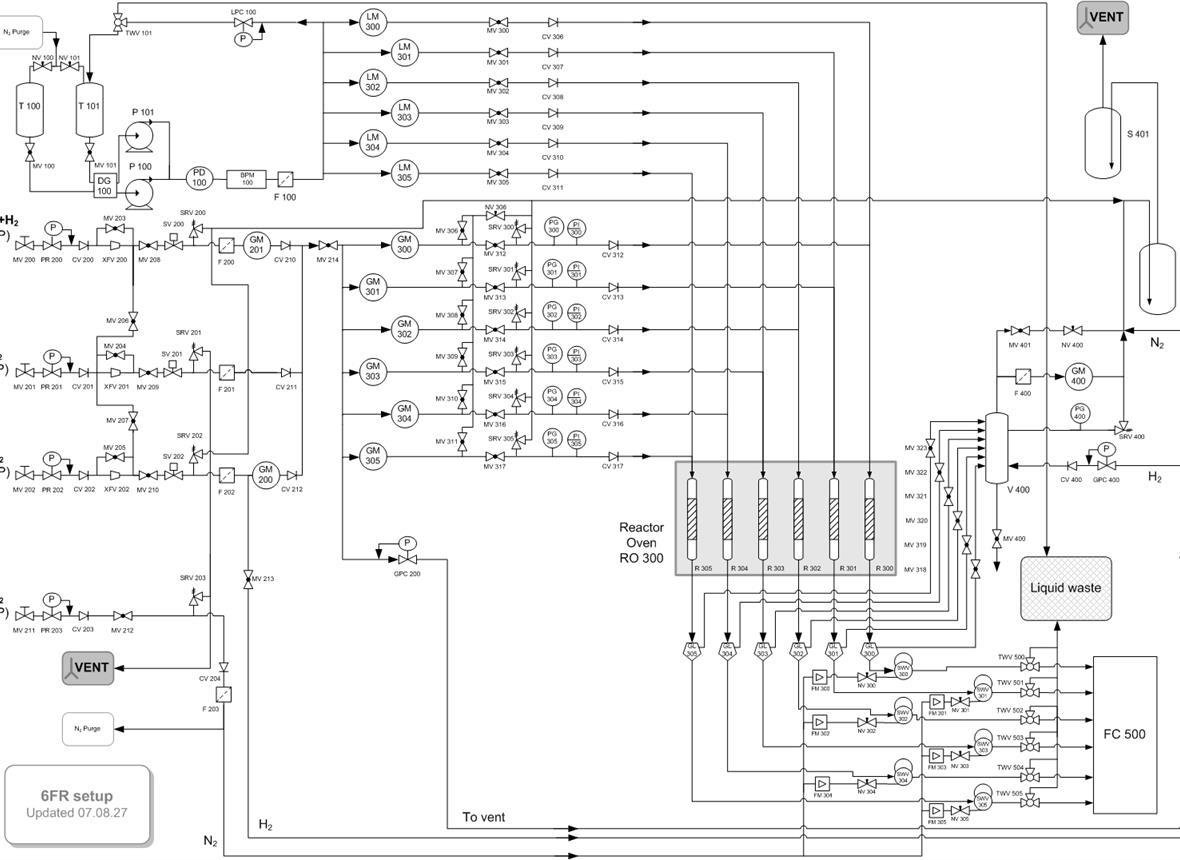
Polyaromatic hydrocarbons, polycyclic aromatics or polyarenes are a major (by-)product fraction of multiple classical, waste, and bio-refinery operations. They have an extremely negative environmental impact, a minimal market, and a lowering demand. Parallelly, lowly alkylated single ring arenes or monoaromatics (benzene, toluene, and xylenes, the so-called BTX fraction) are highly demanded due to their applications as chemicals or fuels. Herein, we review the status of applied polyaromatic selective ring-opening (SRO) by
hydrocracking into monoaromatics. This review addresses the involved mechanisms, applicable catalysts, and reported modeling approaches for SRO. Applying the multivariate analysis to the results reported in the literature using model molecules, we showcase the limitations for extrapolating the obtained knowledge to realistic polyaromatic stream processing. We also provide a statistical evaluation of the suitability of several polyaromatic streams for their SRO processing and assess the markets, usage, and production routes for monocyclic aromatics. Finally, the technologies of these processes are also evaluated and compared, while the most promising one is discussed further based on process simulations and a techno-economic assessment.